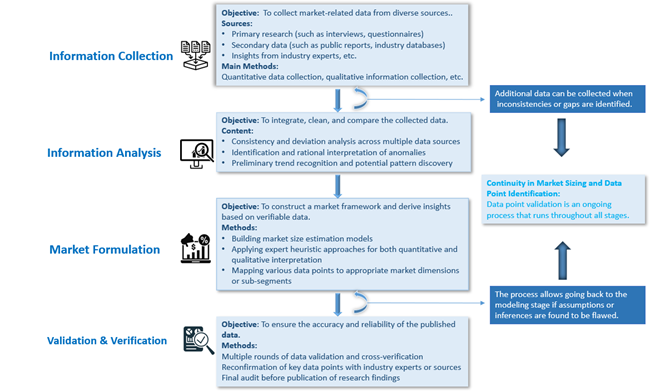
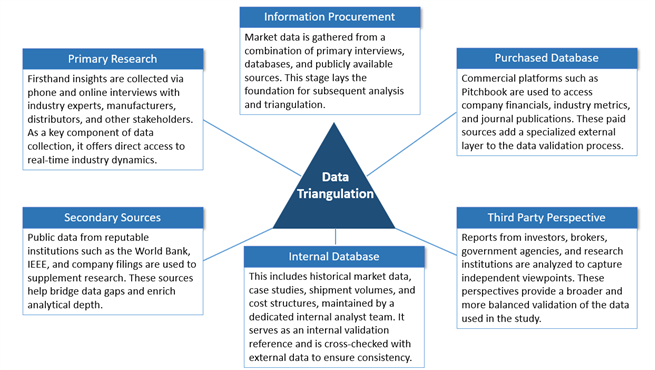
Metallocene PP Market Analysis
Metallocene Polypropylene (mPP) is ahigh-performance polymer synthesized from propylene using metallocene catalystsunder precisely controlled conditions. It exhibits significantly enhancedphysical properties compared to conventional polypropylene, offering wideapplication potential across various industries.
Compared to traditional polypropylene, mPP boastssuperior optical clarity, impact resistance, and stiffness. These attributesmake it especially suitable for applications demanding both aesthetic appealand durability, such as packaging, automotive interiors, medical products, andconsumer goods. Owing to its excellent transparency, mechanical strength, andlow levels of volatiles and extractables, mPP is primarily used in nonwovenfabrics, injection molding, and film materials. In the production of nonwovensand films, mPP ensures higher cleanliness and better durability, leading to itswidespread adoption in high-end packaging and healthcare products.
What sets mPP apart is its use of metallocenecatalysts, which represent the fifth generation of catalyst technology. Thesecatalysts enable precise control over the polymer’s molecular weightdistribution, resulting in polymers with more uniform molecular structures andenhanced performance. As a result, mPP exhibits improved tensile strength,flexibility, and transparency.
The production of metallocene polypropylenetypically involves optimized versions of traditional polypropylene productionlines. The most common processes include a combination of bulk phase–gas phaseor pure gas-phase polymerization, which are more complex and costly thanconventional methods—making mPP more challenging to produce. Nevertheless, itsperformance advantages continue to drive growing demand in high-end applicationmarkets.
According to LookWhole Insight, the global MetallocenePP market is projected to reach USD 784.78 Million in 2024. It is expected to grow to USD 1138.42 Million by 2033,registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.22% during the forecastperiod (2025–2033).
Comparisonbetween Metallocene Polypropylene and Traditional Polypropylene
|
Product Type |
Catalyst |
Advantages |
Main Applications |
|
Conventional Polypropylene (PP) |
Ziegler-Natta (Z-N) |
Lightweight, cost-effective, hygienic, high temperature resistance, easy processing |
Filament spinning, injection molding, fiber |
|
Metallocene Polypropylene (mPP) |
Metallocene |
Superior appearance, excellent transparency; lower volatile/extractable content, improved cleanliness |
Non-woven fabrics & spinning, injection molding, film materials |
It is worth noting that in recent years, China hasmade significant breakthroughs in metallocene catalysts and productionprocesses. Enterprises such as CNPC and Sinopec have increased their investmentin the research and development of mPP, which has promoted the progress ofdomestic mPP production technology. Although China's mPP production is still inits infancy and mainly relies on the traditional Ziegler-Natta catalyst system,China has begun to introduce the world's leading polypropylene production processand gradually carry out industrial production. At present, some Chinesepetrochemical companies, such as PetroChina Harbin Petrochemical, SinopecYanshan Petrochemical and Yangzi Petrochemical, have begun industrialdevelopment of mPP models and plan to further develop mPP catalysts and newgrades to enhance their competitiveness in the global market.
mPP Processing Technology
mPPProcessing Technology
|
Category |
Subcategory |
Description |
|
Bulk-Gas Phase Combination Process |
Spheripol |
A polymerization process combining liquid-phase polymerization and liquid-phase homopolymerization with gas-phase copolymerization. Produces spherical PP powder with adjustable particle distribution. Capable of producing a wide range of products with high purity, excellent optical properties, and no odor. |
|
Hypol |
A hybrid process that integrates the advantages of bulk-phase and gas-phase polypropylene polymerization to produce multiple PP grades without deashing or removing random copolymers. Similar to Spheripol, but in Hypol, the homopolymer cannot be bypassed out of the gas-phase reactor, and part of the flashing steam from the high-pressure degasser is recycled back into the gas-phase reactor. |
|
|
Gas Phase Polypropylene Process |
Chisso |
Developed based on Innovene gas-phase process technology, with a simpler design and lower energy consumption. Catalysts have high activity and selectivity, controlling the formation of amorphous polymers while maintaining a high yield of isotactic polymers. The resulting polypropylene has good morphology, low fine powder content, narrow particle size distribution, good flowability, and is easy to transfer to a second reactor. |
|
Novolen |
Developed by BASF, this process uses a vertical reactor with double-helix ribbon agitation to ensure uniform catalyst distribution in the gas-phase monomer. This maintains consistent Ti/Al/Cr co-catalyst ratios for each polymer particle, addressing gas-solid distribution issues. Suitable for producing a wide range of polypropylene products. |
|
|
Sumitomo |
Uses tandem gas-phase fluidized bed reactors. Produces polypropylene with high crystallinity and a broad product range. |
The mPP productionprocess is divided into bulk method-gas phase method and gas phase method,which are more difficult and costly than traditional polypropylene. Mostleading companies use the original polypropylene production line to producemPP, so the processing technology of mPP is mostly optimized on the originalproduction line. The processing technology of mPP is mainly concentrated in thebulk method-gas phase combination process and the gas phase polypropyleneprocess. The control of metallocene catalysts has very high technicalrequirements, and also requires manufacturers to have rich mPP productionexperience. At the same time, metallocene catalysts consume more and are moresensitive to impurities, water and other substances. The mPP production linehas higher requirements for the purity of propylene. Therefore, compared withthe traditional Z-N catalyst production method, the production of mPP is moredifficult and the production cost is also higher.
Global Metallocene PP Market: Competitive Landscape
At present, the global mPP market is dominated by afew large international companies, especially ExxonMobil, TotalEnergies,LyondellBasell and Mitsui Chemicals, which have long-term advantages in theresearch and production of metallocene polyolefin (mPP) technology. Thesecompanies have mastered the mPP technology and production processes worldwide,and due to technological accumulation and scale effects, their market share ismuch higher than other competitors. The production of mPP relies on high-end metallocenecatalyst technology. These companies have occupied a significant share in themarket with their advanced catalysts and production processes. In particular,LyondellBasell and ExxonMobil provide a variety of high-transparency andhigh-fluidity mPP products to meet a wide range of market needs.
Market Report Coverage & Segmentation
The following is a brief introduction of the latestreport released by LookWhole Insight. This reportsystematically compiles global data on the Metallocene PP market, includingproduction capacity, sales revenue, pricing, and future development trends. Itprovides in-depth analysis of various market segments from multipleperspectives—such as key manufacturers, product types, application areas, andregional markets. The report comprehensively examines the productcharacteristics, market positioning, business performance, and market shares ofmajor players in both the global and Chinese markets. It aims to offer athorough and objective market research resource for industry stakeholders,investors, and policy makers. Additionally, it serves as a reliabledecision-making tool for market analysts, investment professionals, andgovernment agencies.
|
ATTRIBUTE |
Details |
|
|
Time Coverage |
Historical Year: 2020– 2024 Base Year: 2024 Estimated Year: 2025 Forecast Year: 2025 - 2033 |
|
|
Market Segmentation |
||
|
By Type |
Homopolymer Copolymer |
|
|
By Application |
Medical and health care Cosmetic packaging Others |
|
|
By Company |
LyondellBasell ExxonMobil TotalEnergies Japan Polypropylene Corporation Mitsui Chemicals LG Sinopec Borouge Yueyang Xingchang Petrochemical |
|
|
By Region |
North America |
|
Chapter 1: Report Scope and Market Definition
This chapter outlines the statistical boundaries and scope of the report. It defines the segmentation standards used throughout the study, including criteria for dividing the market by region, product type, application, and other relevant dimensions. It establishes the foundational definitions and classifications that guide the rest of the analysis.
Chapter 2: Executive Summary
This chapter presents a concise summary of the market’s current status and future outlook across different segments—by geography, product type, and application. It includes key metrics such as market size, growth trends, and development potential for each segment. The chapter offers a high-level overview of the Metallocene PP Market, highlighting its evolution over the short, medium, and long term.
Chapter 3: Market Dynamics and Policy Environment
This chapter explores the latest developments in the market, identifying key growth drivers, restraints, challenges, and risks faced by industry participants. It also includes an analysis of the policy and regulatory landscape affecting the market, providing insight into how external factors may shape future performance.
Chapter 4: Competitive Landscape
This chapter provides a detailed assessment of the market's competitive environment. It covers market share, production capacity, output, pricing trends, and strategic developments such as mergers, acquisitions, and expansion plans of leading players. This analysis offers a comprehensive view of the positioning and performance of top competitors.
Chapters 5–10: Regional Market Analysis
These chapters offer in-depth, quantitative evaluations of market size and growth potential across major regions and countries. Each chapter assesses regional consumption patterns, market dynamics, development prospects, and available capacity. The analysis helps readers understand geographical differences and opportunities in global markets.
Chapter 11: Market Segmentation by Product Type
This chapter examines the market based on product type, analyzing the size, growth trends, and potential of each segment. It helps stakeholders identify underexplored or high-potential product categories—often referred to as “blue ocean” opportunities.
Chapter 12: Market Segmentation by Application
This chapter analyzes the market based on application fields, providing insights into the scale and future development of each application segment. It supports readers in identifying high-growth areas across downstream markets.
Chapter 13: Company Profiles
This chapter presents comprehensive profiles of leading companies operating in the market. For each company, it details sales revenue, volume, pricing, gross profit margin, market share, product offerings, and recent strategic developments. This section offers valuable insight into corporate performance and strategy.
Chapter 14: Industry Chain and Value Chain Analysis
This chapter explores the full industry chain, from upstream raw material suppliers to downstream application sectors. It includes a value chain analysis that highlights the interconnections and dependencies across various parts of the ecosystem.
Chapter 15: Key Findings and Conclusions
The final chapter summarizes the main takeaways from the report, presenting the core conclusions, strategic recommendations, and implications for stakeholders. It encapsulates the insights drawn from all previous chapters.